Your cart is currently empty!

Growing Coffee: The Ultimate Guide to Cultivating the Perfect Brew
Coffee is not just a beverage; it’s a global phenomenon that fuels billions of people daily. The journey of this beloved drink starts with the humble coffee plant, grown in diverse regions around the world. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about growing coffee, from understanding the ideal conditions to exploring different varieties and sustainable farming practices. Whether you’re an aspiring coffee farmer or a coffee enthusiast, this comprehensive guide will help you appreciate the complexities of coffee cultivation.
Ideal Conditions for Growing Coffee
Climate Requirements
Coffee thrives in tropical climates, where temperatures range between 60°F and 70°F (15°C and 24°C). The perfect environment combines warmth with consistent rainfall, making regions like India, Brazil, and Ethiopia prime locations for coffee cultivation. Shade is another critical factor—many farmers grow coffee under a forest canopy to protect the plants from direct sunlight, ensuring slow growth that enhances flavor.
Soil Requirements
Coffee plants prefer loamy, well-drained soils rich in organic matter. The ideal soil pH ranges from 6 to 6.5, slightly acidic but not overly so. Adding organic compost and fertilizers helps maintain nutrient levels, providing the essential minerals coffee plants need to thrive.
Coffee Plant Varieties
Arabica vs. Robusta
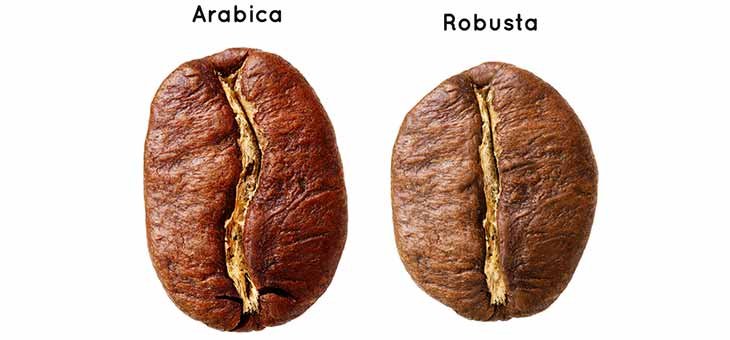
The two most popular varieties of coffee are Robusta and Arabica.. Arabica is known for its smooth flavor and lower caffeine content, making it a favorite among specialty coffee lovers. In contrast, Robusta has a stronger, more bitter taste and higher caffeine content, often used in blends and instant coffee. Explore the rich flavors of Arabica and Robusta in Malenadu Coffee Powder from Malenadu Taste and Travel.
Specialty Varieties
Beyond Arabica and Robusta, there are specialty coffee varieties like Liberica and Excelsa. These beans are known for their unique flavors and aromas, offering a distinct coffee experience. Specialty coffee enthusiasts may also appreciate the rare and exotic flavors found in Gourmet Coffee.
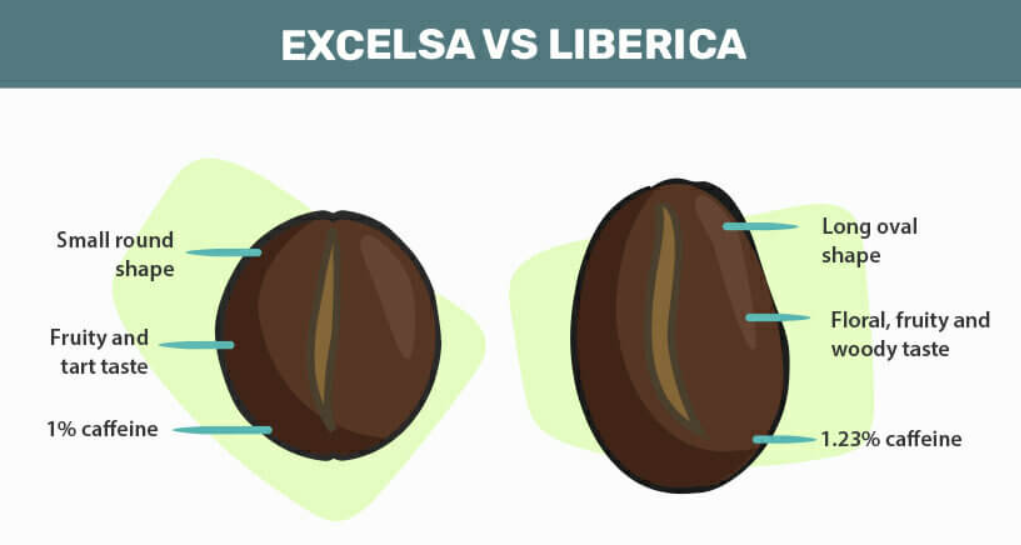
Varieties in India
India is home to several unique coffee varieties, particularly in regions like Chikkamagalur, Coorg, and Wayanad. These regional varieties offer distinct flavor profiles influenced by local climates and soils. Discover the essence of Indian coffee with the Malenadu Coffee Powder collection.
The Coffee Growing Process
Propagation Methods
Coffee plants can be propagated through seeds or cuttings. While seeds are the most common method, cuttings offer a quicker route to producing coffee, ensuring consistency in the quality of the plants.
Planting

The process begins in a nursery, where seeds are carefully nurtured until they sprout. Seedlings are then transplanted into the field once they reach an adequate size. Proper spacing and care during transplantation are crucial for healthy plant development.
Coffee Plant Growth Stages
Coffee plants go through several growth stages, including germination, vegetative growth, flowering, and fruiting. Each stage requires specific care, from ensuring proper water supply to protecting the plants from pests and diseases.
Coffee Farming Practices
Traditional vs. Modern Farming Techniques
Traditional coffee farming often involves agroforestry and organic farming practices, where coffee plants grow alongside other crops and trees. Modern techniques, such as permaculture, focus on sustainability and maximizing yield while minimizing environmental impact.
Irrigation and Water Management
Effective irrigation is vital for coffee plants, especially in regions with inconsistent rainfall. Water conservation methods, such as drip irrigation, help maintain soil moisture levels without overusing water resources.
Fertilization and Pest Control
Coffee plants benefit from organic fertilizers like compost and manure, which improve soil health over time. Pest control can be managed through natural methods, but in some cases, chemical treatments may be necessary to protect crops from common threats like coffee rust and the coffee borer beetle.
Harvesting Coffee
When and How to Harvest
Coffee cherries are typically harvested when they reach full ripeness, indicated by a deep red color. The timing of the harvest significantly impacts the flavor and quality of the coffee.
Harvesting Techniques
Hand-picking is the most common method, especially for specialty coffee, as it allows for selective harvesting of only the ripest cherries. In contrast, mechanical methods are often used in large-scale operations but may sacrifice some quality for efficiency.
Post-Harvest Processing
After harvesting, coffee cherries undergo wet or dry processing to extract the beans. Wet processing involves fermenting the cherries in water before drying, while dry processing skips the fermentation step, leading to different flavor profiles. Learn more about these processes in our Ultimate Guide to Black Coffee.
Coffee Growing Regions in the World
Overview of Global Coffee Production
The world’s leading coffee-producing countries include Brazil, Vietnam, and Colombia. These regions benefit from ideal climates and extensive coffee-growing experience, contributing to their dominance in global coffee markets.
Coffee Growing in India
India has a rich history of coffee cultivation, with major coffee-growing states like Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. Regions such as Chikkamagalur and Coorg are renowned for their unique coffee varieties, offering distinctive flavors that reflect the local environment. Explore the Malenadu Taste and Travel Coffee Powder to experience the essence of these regions.
Sustainable Coffee Farming
Environmental Impact of Coffee Cultivation
Coffee cultivation can have significant environmental impacts, including deforestation, water usage, and biodiversity loss. These issues are particularly pressing in regions where coffee farming is expanding into new areas.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainable coffee farming practices, such as shade-grown coffee, organic certifications, and fair trade, are essential for minimizing environmental impact and supporting the livelihoods of coffee farmers. These methods not only protect ecosystems but also produce high-quality coffee. Learn about sustainable farming in our Exploring the Magic of Coffee Plantations guide.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Coffee Farming
Technology plays a vital role in modern coffee farming, with innovations like precision agriculture, remote sensing, and automation helping farmers optimize their operations and reduce environmental impact. These tools allow for more efficient water use, better pest management, and improved crop yields.
Challenges in Coffee Growing
Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to coffee production, affecting both the quality and quantity of coffee yields. Rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and increased incidences of pests and diseases are major challenges that coffee farmers must navigate.
Economic Challenges
The coffee industry faces several economic challenges, including price fluctuations, labor costs, and market access. These factors can make it difficult for small-scale farmers to sustain their operations, especially in volatile markets.
Pests and Diseases
Common pests and diseases like coffee rust and the coffee borer beetle can devastate coffee crops if not managed properly. Integrated pest management strategies, including both organic and chemical controls, are essential for protecting coffee plants.
Future of Coffee Growing
Innovations in Coffee Cultivation
The future of coffee growing lies in new varieties, breeding techniques, and genetic research. These innovations aim to create more resilient coffee plants that can withstand the challenges posed by climate change and pests.
The Role of Consumer Demand
Consumer preferences are shifting towards more sustainable and ethically produced coffee. This trend is driving changes in farming practices, with a growing emphasis on quality and sustainability. Discover how consumer demand shapes the industry in our Guide to Running a Successful Coffee Company.
Coffee Farming in a Warming World
As the planet warms, coffee farmers must adopt adaptation strategies to protect their crops and ensure future coffee production. These strategies include planting in higher altitudes, developing drought-resistant varieties, and implementing advanced farming techniques.
Conclusion
Growing coffee is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of the plant, the environment, and sustainable farming practices. By supporting ethical coffee brands and exploring the world of coffee cultivation, you can contribute to a more sustainable future for this cherished beverage.

